Data Governance Supporting tagline
What is Data Governance?
Is a set of principles and practices that ensure high quality data to meet information needs of stakeholders.
What does it solve?
- Confusing data
- Multiple versions of truth
- Unclear ownership
- Legacy data
- Unknown context of data
- Lack of documentation
Component of Data Governance
- Standards: Company policies defining format, definition, structure, manipulation and user of data
- Catalog: Inventory of the data assets
- Architecture: Technical decisions about setting up the framework to govern data
- Quality: Reliability of data
- Policy: Rules about lawful handling of data
- Security: Labeling and protecting confidential data
Types of Data Governance
Centralized model
Top down approach of data governance. A central repository which receives and shares data among other domains of the organization Cons: Bottlenecks and delays since the responsibilities lies with centralized team
De-Centralized model
Opposite to centralized. Data governance is handled by individual domain teams. Cons: risk of inconsistencies negating the impact of governance efforts.
Federated model
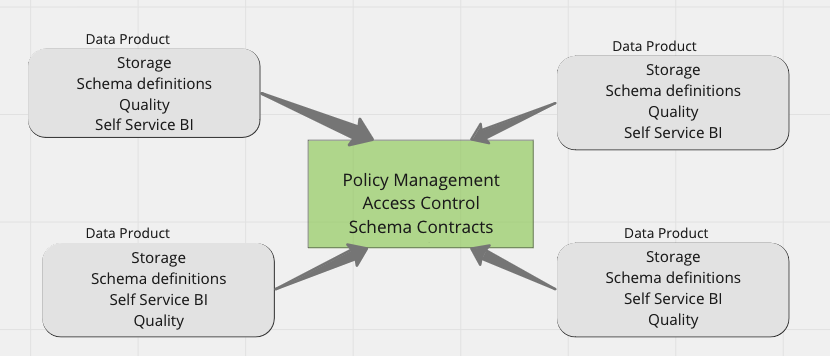
Centralized standards and policies but automomy of executing these standards lies with individual domain teams. Domain teams own data and a use a shared data infrastructure to build data products.Access and data contracts etc are managed centrally.
Published
07 March 2023